Pediatric Tonsil Infection
Tonsil infections are a common childhood malady, bringing pain and discomfort to many children. The result of inflamed tonsils, the condition—known as tonsillitis—is most often caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
What Causes Tonsil Infections?
The tonsils are a pair of oval-shaped tissues in the back of the throat. They protect the body from infection by trapping bacteria and germs, preventing them from entering the airways. In addition, they produce antibodies to fight infection. As part of the immune system’s first line of defense, the tonsils come into frequent contact with germs, making them prone to infection themselves.
Viruses and bacteria, especially the Streptococcus bacterium (responsible for strep throat), are the most common causes of tonsillitis. Other causes include adenoviruses, influenza, Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, and herpes simplex virus.
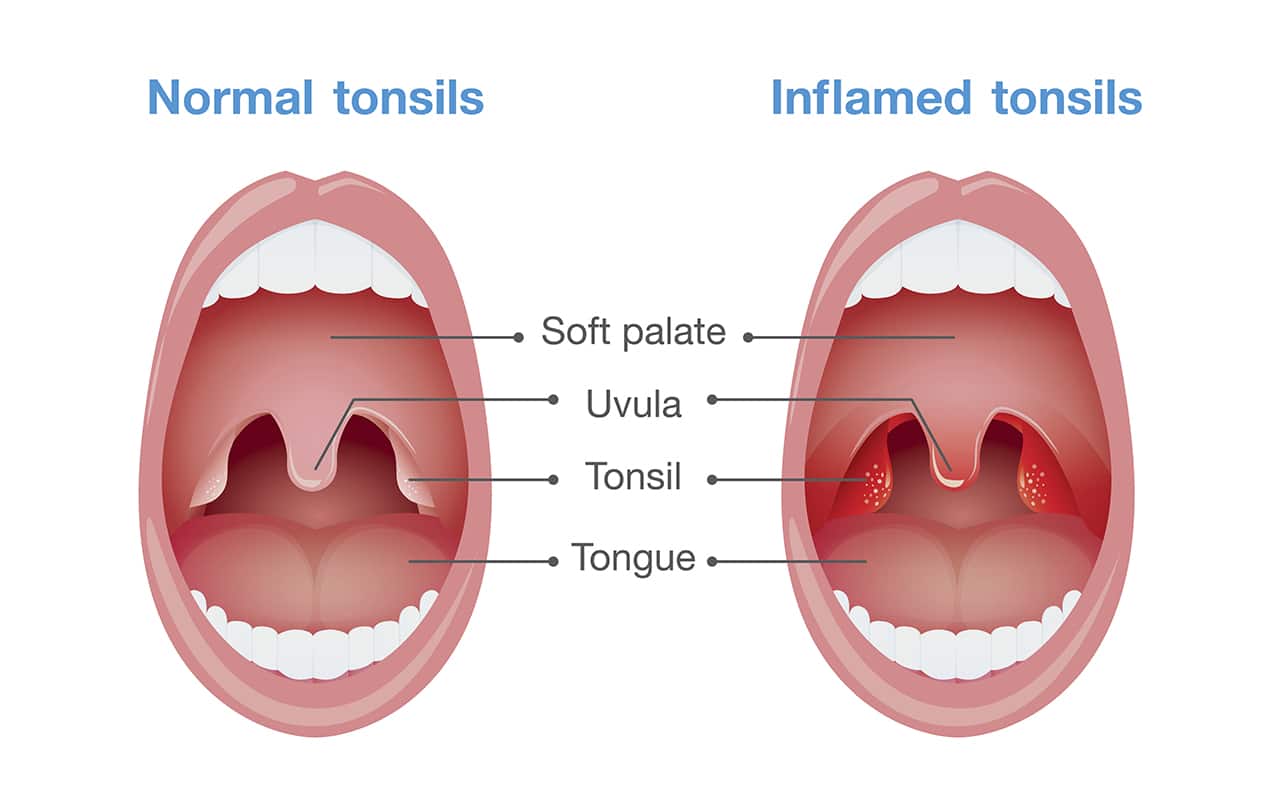
What Are the Symptoms and Signs of Tonsil Infections?
Symptoms may include:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Ear pain
- Bad breath
Signs may include:
- Swollen, red tonsils
- White or yellow coating
- Blisters on the throat
- Swollen glands in the neck or jaw
- Fever and/or chills
How Are Tonsil Infections Treated?
Diagnosing a tonsil infection requires a physical examination and an in-depth exam of the throat and ears with an otoscope. Your child is likely to be given a throat swab to test for the presence of strep, as well.
During an acute infection, home remedies can be effective for tonsil infections caused by a virus. Your child should get plenty of rest and stay hydrated with fluids. Warm broth or herbal tea can help them stay hydrated when they don’t feel like eating or cannot due to the pain, and cold Popsicles are particularly effective at soothing pain and discomfort. Pain and fever can be controlled with over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen and acetaminophen (but avoid aspirin, which can be harmful in children). When a tonsil infection is the result of strep throat or another bacterial infection, your child’s doctor will prescribe antibiotics. Be sure to help them take the full course of treatment to prevent symptoms from recurring.
For chronic or recurrent cases of tonsillitis, surgical removal can be considered (tonsillectomy). The decision for this procedure also typically includes making sure your child has been treated adequately for the acute infections along with any underlying conditions that could be making them at risk for infection.
If you’re dealing with repeated sore throats that don’t seem to end, or if you’re wondering what treatment options are right for your child, call DeFatta ENT & Allergy at (715) 828-2368 for more information or to schedule an appointment